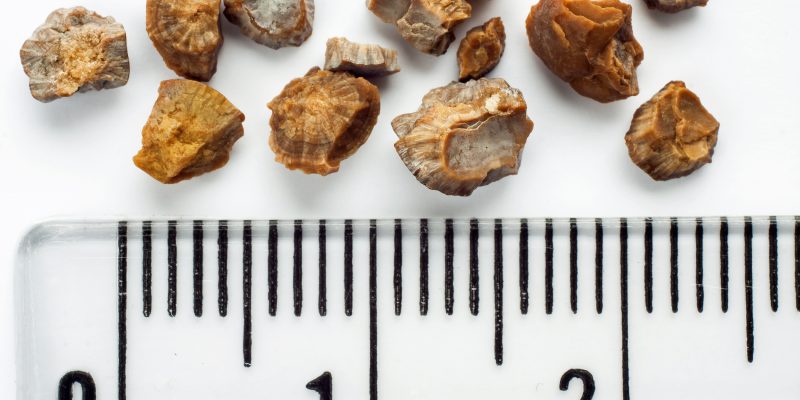
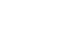KIDNEY STONES: WHAT ARE THEY?
Kidney stones are “small stones” made up of different substances (calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, uric acid etc.) that are formed in the kidneys but which can be found at any level of the urinary system.
Symptoms
As long as the stones remain in the kidneys, there are no major symptoms (mild back pain and stinging pains). When the stones descend into the ureter they cause renal colic with violent pain, and sometimes nausea, vomiting and sweating that leads to the emergency room.
Colic
In the course of renal colic, violent pain radiates into the groin and lumbar regions. Therapy includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatories, pain relievers and antispasmodics. Alpha blockers may be useful to facilitate the expulsion of the stone.
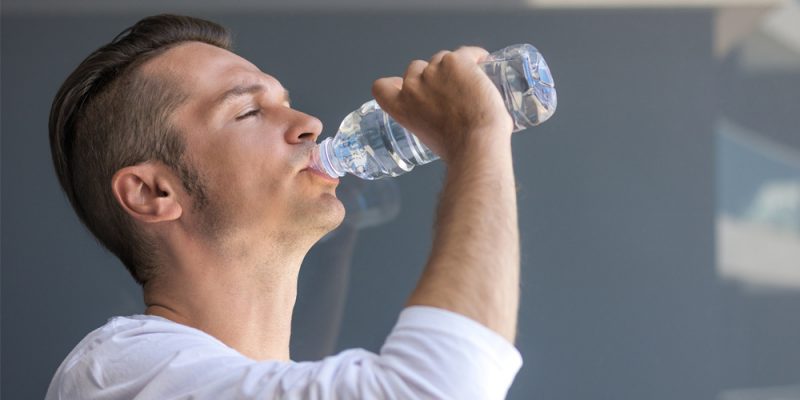

KIDNEY STONES: THE CAUSE
Kidney stones are very common, it is estimated that there are about 100.000 new cases a year with a higher frequency in the regions of Southern Italy.
But what are the predisposing factors? One reason is the heat, in fact it has been shown that high outside temperatures, especially when associated with dehydration from exercise and a high consumption of sugary drinks can increase the risk of kidney stones.
The high frequency of cases also depends on other risk factors such as obesity, a sedentary lifestyle and a high-protein diet which is low in fruit and vegetables.
Obviously, family history is of great importance and must always be considered. Other elements favouring the formation of stones? Definitely not drinking enough, because water prevents the substances that form stones from crystallization and precipitating.
THE NATURE OF KIDNEY STONES
In the presence of renal colic with excruciating pain, we often proceed with an ultrasound of the abdomen or a CT scan to better identify the stones and evaluate their location, size and assess the density. Depending on the type of stone, it is then decided whether to intervene or not. If the obstruction is important, it is done by inserting a catheter between the kidney and the bladder in order to “bypass” the stone and avoid any kidney blockage.
If, on the other hand, the stone is smaller than a centimetre and there are no complications, it is preferable to wait for the patient to pass it by himself within a few days.
If the stone is not eliminated spontaneously, extracorporeal lithotripsy can be used, which acts from the outside through shock waves and breaks the stone, thus facilitating its exit. In the case of larger stones, it is preferable to resort to urological endoscopy techniques.
The urethra is entered using an endoscope and pulverizes the stone in place and then “vacuums” up the dust, or percutaneous surgery is chosen if the stone exceeds two centimetres, eliminating it directly with a nephroscope equipped with a laser.
Once the stone has been eliminated, a metabolic evaluation is necessary to understand the composition of the stone. Each of us, in fact, always produces the same type of stone and knowing which form the individual patient has is essential in giving different dietary and therapeutic indications depending on whether the stones contain calcium oxalate (the most common), calcium phosphate, uric acid or cystine.
In many cases it is enough to change the acidity of the urine, sometimes too acidic, to prevent new stones forming or to favour dissolving the stones. In this case CITRATES and FILLANTO (officinalis plant) are extremely important.
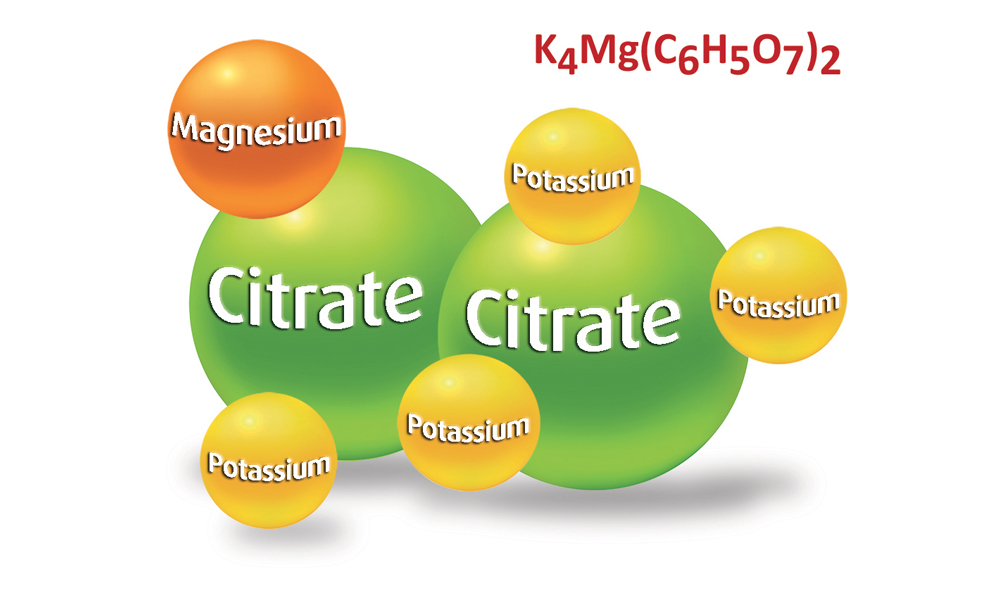
CITRATES
Citrates (usually magnesium citrate and potassium citrate) are salts that play a fundamental role in the prevention and therapy of kidney stones. Citrates perform two main actions:
1-due to their alkaline characteristics, they are useful in raising the urinary pH (i.e. reducing its acidity) and consequently promoting the solubilization of uric crystals.
2-thanks to their ability to bind and sequester calcium, they act on calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate stones, transforming them into a solubilized form.
CITRATES: THE INNOVATION OF COMBINED SALT
Combined Potassium-Magnesium salt is a particular saline complex in a single formula which, compared to the more common mixtures of potassium citrate and magnesium citrate, contains greater quantities of citrate and therefore has greater effectiveness.
It also contains potassium and magnesium in the correct ratios to maintain optimal muscle, heart and nervous system functions.
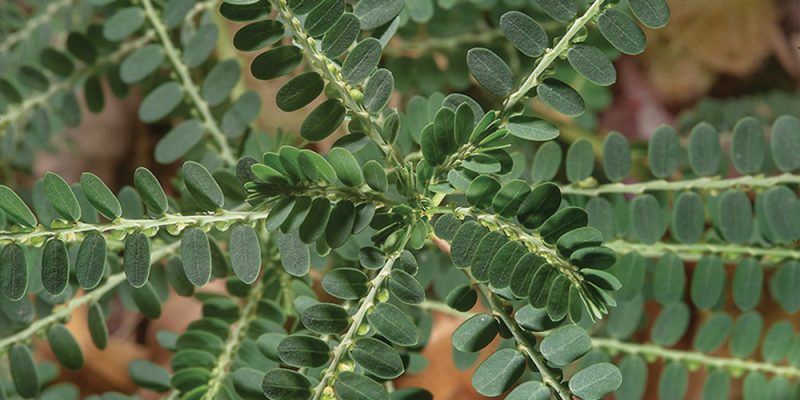

THE FILLANTO
Phyllantus niruri (Fillanto) is a typical plant from South America also known by the Peruvian name “Chanca Piedra” that means “destroyer of stone”.
An extract rich in tannins is obtained from the flowers and leaves of this plant, characterized by an important activity. It is able to counteract lithiasis, that is the formation and aggregation of kidney stones by increasing the solubility of alkaline salts and helping to keep the bacterial rate of the urogenital tract low. It also promotes the expulsion of the stones themselves and the gravel (kidney sand) as it has a relaxing action on the smooth muscles of the urogenital tract.
Results of clinical studies have shown that Fillanto has a good therapeutic potential since it is able to modify the consistency and structure of the stone making it more brittle and therefore easily disintegrated and eliminated in the urine.
For further information, please use the contact form which is available via the menu at the top of the page.